8p Genetics

Chromosome 8p is a rare genetic condition with approximately 1 in 10,000 patients around the world and counting. A chromosome disorder typically impacts every cell in your body, not just in one organ of your body, but often your entire human system. Right now, science does not have the means to treat this condition. The good news is that the scientific community is making substantial progress and together with Project 8p, we are going to do everything we can to help.
In most cases, Chromosome 8, appears to result from spontaneous (de novo) errors very early in embryonic development that occur for unknown reasons and are not inherited. Recently, we have found families where the mutation has also been inherited but different manifestations of the symptoms.
What is a chromosomal disorder?
Chromosomal rearrangements differ in structure or copy number (copy number variants) from what would be the Norm called disomy with two copies. Anything different from two normal copies results in a disorder such as:
- Monosomy – A person has only one copy of a chromosome. In a partial monosomy, only part of one chromosome is missing.
- Trisomy – A person has three copies of a chromosome. Partial trisomy means a person has an extra copy of part of a chromosome.
- Deletions– A section of a chromosome is missing. This can be referred to as a deletion, partial deletion, partial monosomy, distal monosomy or terminal deletion.
- Duplications – Part of the chromosome is duplicated so a person has extra genetic material.
- Translocations – A section of one chromosome is transferred to a different chromosome.
- Rings – A portion of a chromosome has broken and formed into a ring shape. This can happen with or without loss of genetic material.
- Mosaicism – Mosaicism occurs when a person has two or more cell populations with a different chromosomal makeup. When abnormalities occur after fertilization, mosaicism can occur because some cells have the abnormality and some do not.
- Isochromosome – This occurs with improper division of the centromere. Isochromosomes contain either two short arms or two long arms, instead one short arm and one long arm, like a typical chromosome.
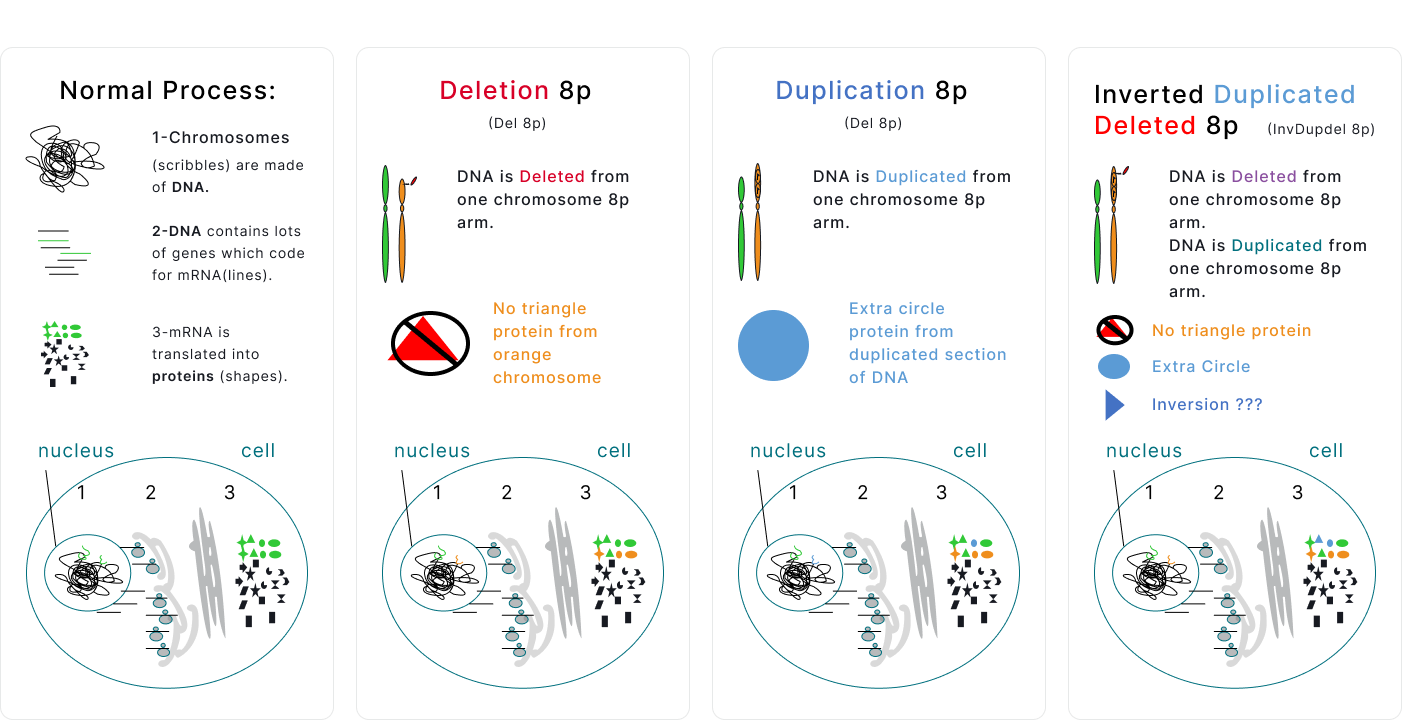
- Inversion – Part of a chromosome has broken off, turned upside down and reattached itself. Inversions can be paracentric or pericentric. Paracentric inversions occur on only one arm of the chromosome and do not include the centromere. Pericentric inversions include the centromere and include both arms of the chromosome.
There are many synonyms of Chromosome 8p diagnoses:
- 8p – Syndrome, Partial
- Chromosome 8p inv/del/dup
- Chromosome 8, 8p Deletion or Del(8p) Syndrome, Partial
- Chromosome 8, Partial Deletion of Short Arm
- Chromosome 8, Partial Monosomy 8p
- Chromosome 8, 8p Duplication or Dup(8p) Syndrome, Partial
- Distal 8p Monosomy
- Partial 8p Monosomy
- Terminal 8p- Syndrome (8p21 to 8p23-pter), Included
- Trisomy 8p
- Mosaicism 8p
Fun Fact: Parts of chromosome 8 have a high rate of mutation and it is one of the chromosomes that differs the most from chimpanzees. Mutations on chromosome 8 may be partially responsible for humans’ large brains so human intelligence can be at least partially traced to people who have mutations and abnormalities on chromosome 8. Chromosomal mutations and abnormalities occur naturally and are the vehicle by which evolution is possible.
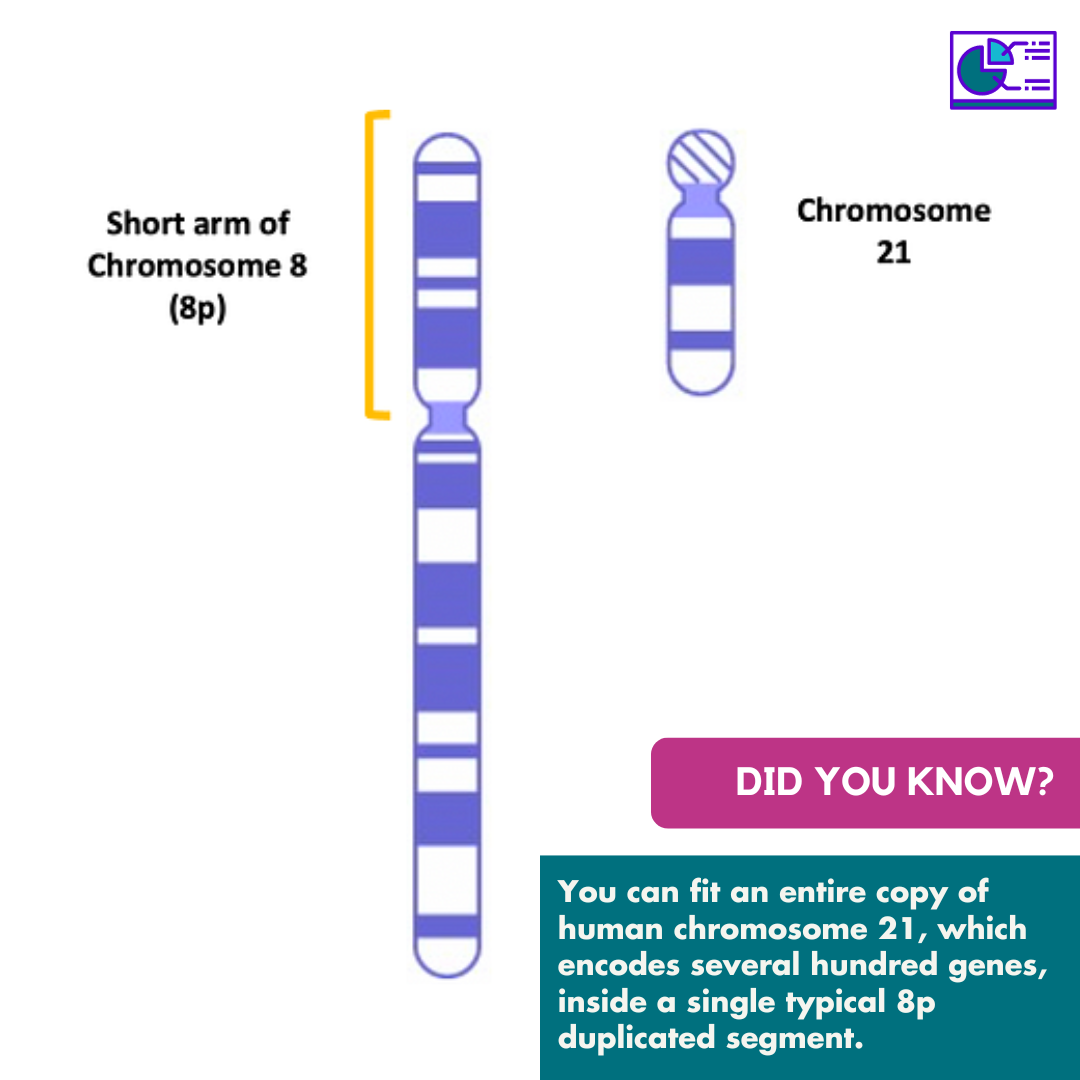
Chromosome 8 contains around 4.5 to 5 percent of the total DNA in cells, which is probably around 700 genes up to 1400 genes.Chromosome 8 contains about 146 million base pairs or DNA building blocks, of which over 95% have been determined
How is 8p Diagnosed?
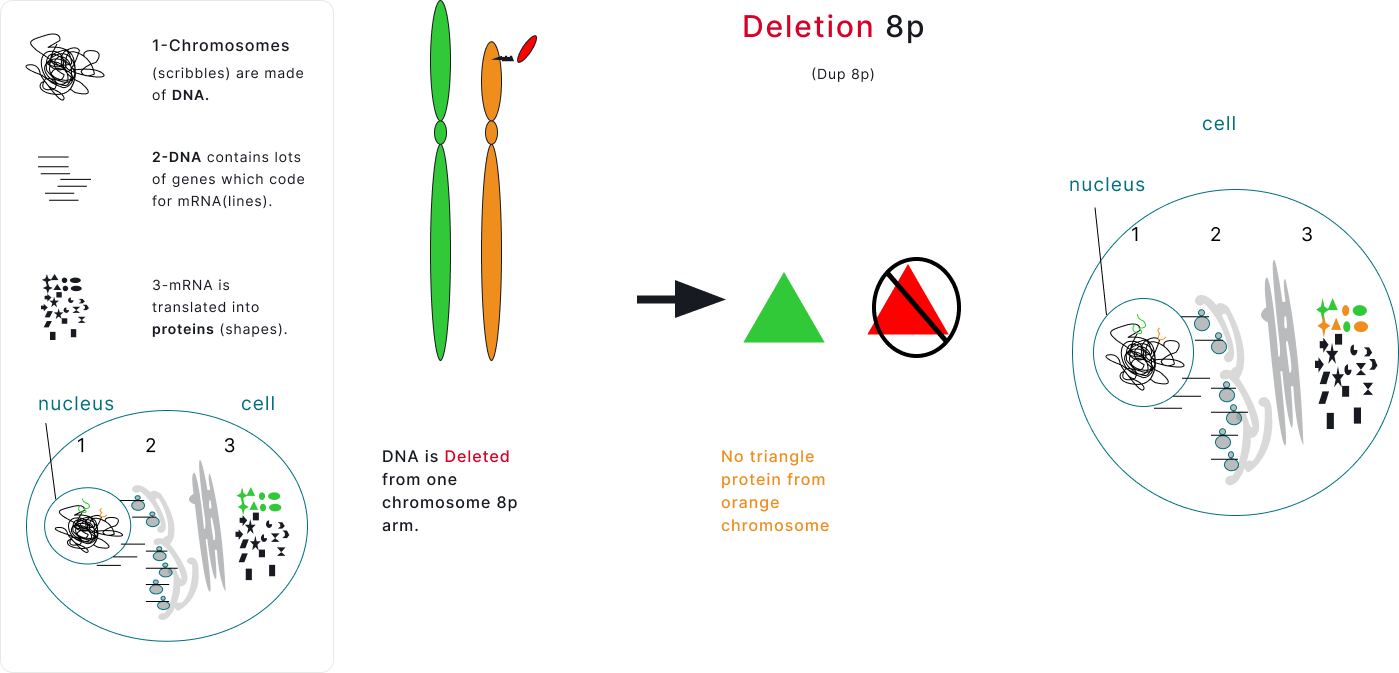
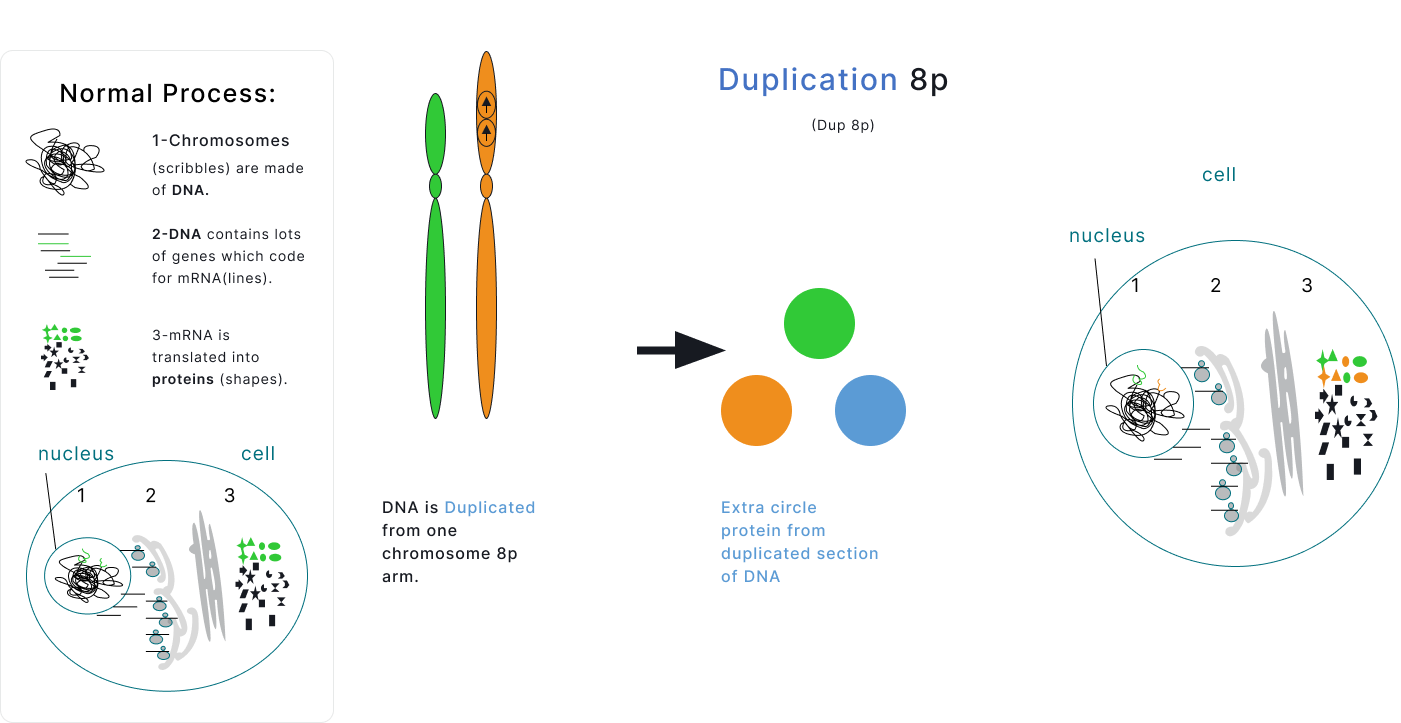
Gene Dosage
Compare the unaffected Chromosome 8 on the left to the affected chromosomes on the right.
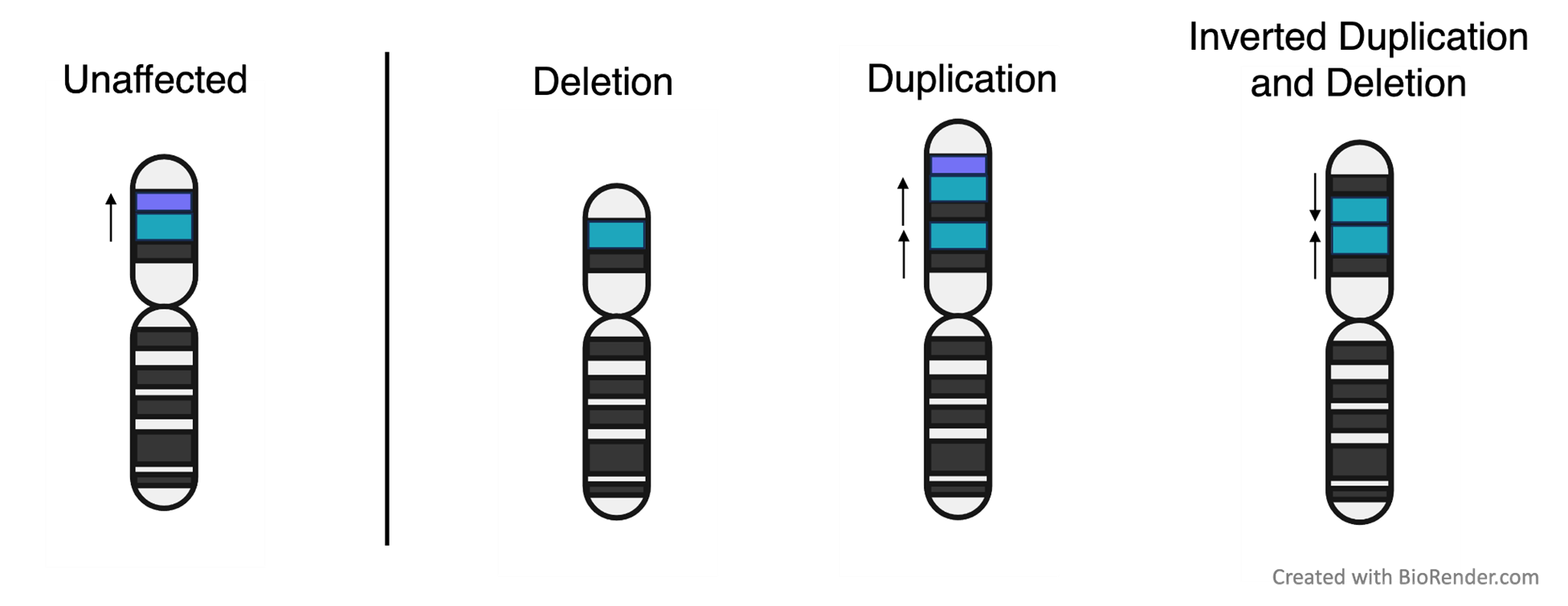
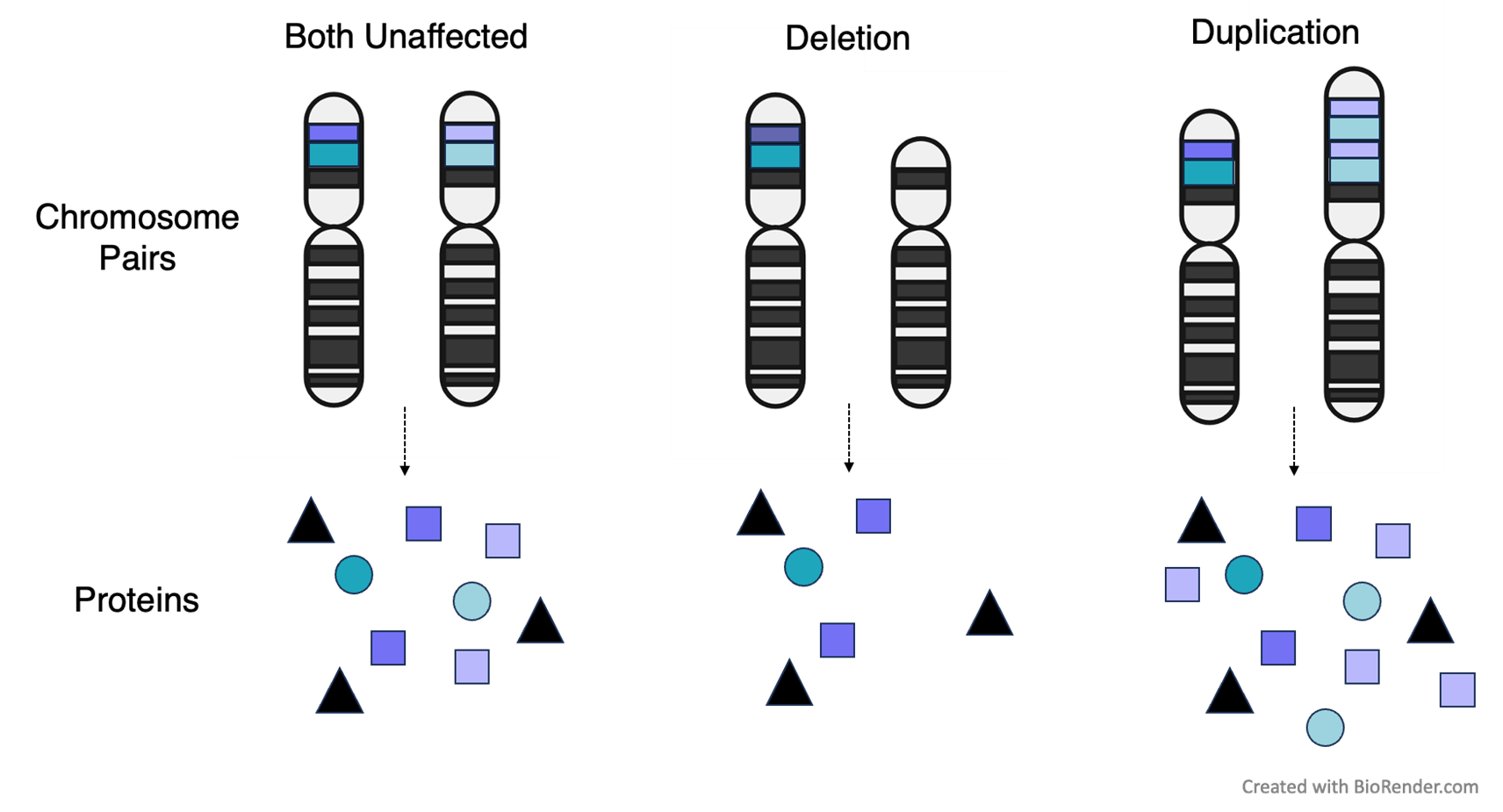
Each cell has two copies of Chromosome 8, one from Mom and one from Dad. One of the copies is unaffected and one has a deletion or duplication. Proteins are made from both of the chromosomes in each pair. Deletion will result in fewer proteins from the deleted region being made, and duplication will result in more proteins from the duplicated region being made. However, cells can respond in unique ways to changes in DNA copy number, so the relationship is not always 1 to 1.
Scroll

Each cell has two copies of Chromosome 8, one from Mom and one from Dad. One of the copies is unaffected and one has a deletion or duplication. Proteins are made from both of the chromosomes in each pair. Deletion will result in fewer proteins from the deleted region being made, and duplication will result in more proteins from the duplicated region being made. However, cells can respond in unique ways to changes in DNA copy number, so the relationship is not always 1 to 1.